NUTRITION
Nutrition is the process by which living organisms obtain and utilize food materials necessary for growth, and energy.
Nutrition is the process by which living organisms obtain and utilize food materials necessary for growth, energy, repair of tissues, and regulation of body processes.
It involves ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion.
CLASSES OF FOOD SUBTANNCES
Foods eaten by animals are generally classified into seven i. e.
1. Carbohydrate
2. Proteins
3. Fat and oil
4. Mineral Salt
5. Vitamins
6. Water
7. Roughages
CARBOHYDRATE
This is gotten from food like bread, yam rice etc. It basically consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Importance of Carbohydrates
a. It gives animals energy.
b. It provides heat needed to maintain body temperature
c. It can be used for lubrication e.g mucus.
d. It provides the body with a strong framework e.g. exoskeleton in insects.
PROTEINS
Protein is made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes phosphorus and sulphur. Food like egg, meat, fish, beans etc gives you protein.
Importance of Proteins
a. Growth in young ones.
b. Repair of worn-out tissues.
c. Production of enzymes.
d. Production of hormones.
e. It supports reproduction.
f. It is for tissue and all formation i.e body building.
FATS & OIL (LIPIDS)
Fats are solid lipids at room temperature while oil is the liquid. Fat and oil consist of carbon, hydrogen and little oxygen. Foods like palm oil, groundnut, Soya beans give fat and oil.
Importance of Fat and Oil
It gives you energy even more than carbohydrates
It supplies essential fatty acids to the body.
It helps in the maintenance of body temperature
It provides the body with fat-soluble vitamins
MINERAL SALT
These are usually taken in very small quantity in the food we eat. The minerals include calcium, magnesium, potassium, Phosphorus, sulphur, chlorine, iron, Iodine, fluorine, manganese, copper, cobalt and sodium.
Importance of Mineral Salts
a. Regulate body metabolisms
b. Components of bones and teeth
c. Aids blood formation
d. Control chemical reactions in the body
e. Aids the formation of enzymes and pigment
VITAMINS
These are organic food substances needed by man and other animals in small quantity for normal
growth and development. Vitamins are grouped into:
1. Water-soluble vitamins include: vitamins B complex and vitamin C. Vitamin B complex include
vitamin, B2, B3 , B5, B6 and B12
2. Fat-soluble vitamins include vitamins A, D, E and K.
Importance of Vitamins
1. Support immune system
2. Enhances growth and development
3. It enhances vision.
WATER
This is of utmost importance to all organisms and it is made up of two elements, hydrogen and
oxygen.
IMPORTANCE OF WATER
a. Metabolic activities of the body of animals.
b. Digestion of food.
c. Maintenance of body temperature.
d. It is a medium of transportation for all nutrients.
e. It helps to maintain the osmotic balance in body tissues.
f. It helps in excretion of metabolic waste from the body e.g urine.
ROUGHAGES
These are indigestible fibrous materials got from vegetables, fruit, carbohydrates and proteins.
Importance of Roughages
1. It aids digestion
2. It helps to avoid constipation.
BALANCED DIET
Balanced diet is a diet containing a correct proportion of all the food substances. On a general note, a
balanced diet contains 15% protein, 15% fat and oil, 10% vitamin, minerals and water and 60%
carbohydrate. Once a food is taken at these proportions, there is a normal growth and development in
the body.
FUNCTIONS OF BALANCED DIET
1. It makes us healthy.
2. It gives ability to be resistant to diseases
3. It makes available energy needed to carry out all biological activities.
4. It prevents malnutrition and deficiency symptoms. For examples, a diet that lacks protein results into a nutritional disease called kwashiokor in children.
MAMMALIAN TEETH
TYPES OF TEETH
The teeth in mammals are of four major types:
1. Incisors: Flat, chisel-shaped with a sharp edge. They are used for biting food, cutting and holding
onto a prey to prevent its escape.
2. Canine: similar to the incisors. They are sharp and pointed at the tips. They are used for tearing
flesh and for catching a prey.
3. Premolars: They are large with rigid flat surfaces which are used for chewing food.
4. Molars: They are used for grinding and chewing food together with the premolar.
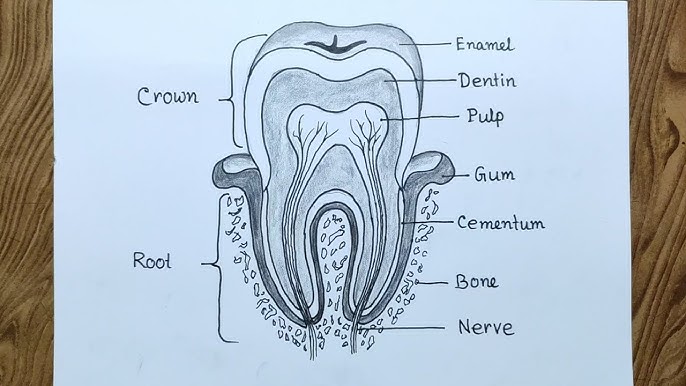
STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH
The mammal’s tooth is divided into three regions
The crown which projects above the gum
The root which is embedded in the jaw bones.
The neck which is the junction between the crown and the root
STRUCTURE OF THE TOOTH
The centre of the tooth consists of a pulp cavity which contains blood vessels and nerves. These are
extremely sensitive to heat and cold. A layer of dentine encloses the pulp. Dentine is a hard and
bone-like material which contains some living cytoplasm. The enamel is a white layer covering the
dentine and is the hardest material made by animals. Enamel protects the pulp and the dentine. A
layer of cement covers the dentine in the root region.
DENTITION
Dentition is the number, arrangement and conformation of teeth in an organism. The teeth are
arranged and fixed to the lower and upper jaw bone.
Types of Dentition
1. Homodont dentition: that is when organisms have the same type of teeth.. All the teeth are of the
same shape, size and function. This dentition is found in fishes, amphibians and reptiles.
2. Heterodont dentition: In this type, organisms have teeth of different shapes, sizes and functions. This observed in mammals.
The type of teeth possessed by an animal is closely related to the type of food it eats.
DENTAL FORMULA
A formula expressing the number and kinds of teeth possessed by a mammal. A dental formula is
usually written in the form of four ‘fractions’,
Man………….2[ I=2/2, C=1/1, P=2/2, M=3/3] = 32.
Dog …………… 2[ I=3/3, C=1/1, P=4/4, M=2/3] = 42.
Cow …………….2[ I=0/3, C=0/1, P=3/3, M=3/3] = 32.
Lion…………… 2[ I=3/3, C=1/1, P=3/2, M=1/1] = 30.
Rabbit …………… 2[I= 2/1, C= 0/0, P=3/2, M=3/3] =28.
Sheep …………….. 2[I=0/3, C=0/1, P= 3/3, M= 3/3] =32.
Rat …………….. 2[I=1/1, C= 0/0, P=0/0, M=3/3] = 16
DIGESTIVE ENZYMES
Enzymes are organic (protein) catalysts produced by living cells which help to speed up and slow
down the rate of chemical reactions. Digestive enzymes aid the breaking down of complex food
substances into simple, soluble and diffusible form.
Characteristics of Enzymes
a. Enzymes are soluble
b. Enzymes are protein
c. They are specific in their actions
d. Enzymes are sensitive to temperature i. e. they work best between 35oC to 40oC
e. Enzymes are PH specific
f. Enzymes brings about reversible reactions
g. Enzymes needs co-enzymes to activate them and can be inactivated by inhibitors such as mercury and
cyanide.
repair of tissues, and regulation of body processes.
It involves ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion
CLASSES OF FOOD SUBTANCES
Foods eaten by animals are generally classified into seven i. e.
1. Carbohydrate
2. Proteins
3. Fat and oil
4. Mineral Salt
5. Vitamins
6. Water
7. Roughages
CARBOHYDRATE
This is got from food like bread, yam rice etc. It basically consists of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
Importance of Carbohydrates
a. It gives animals energy.
b. It provides heat needed to maintain body temperature
c. It can be used for lubrication e.g mucus.
d. It provides the body with a strong framework e.g. exoskeleton in insects.
PROTEINS
Protein is made up of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sometimes phosphorus and sulphur. Food like egg, meat, fish, beans etc gives you protein.
Importance of Proteins
a. Growth in young ones.
b. Repair of worn-out tissues.
c. Production of enzymes.
d. Production of hormones.
e. It supports reproduction.
f. It is for tissue and all formation i.e body building.
FATS & OIL (LIPIDS)
Fats are solid lipids at room temperature while oil is the liquid. Fat and oil consist of carbon, hydrogen and little oxygen. Foods like palm oil, groundnut, Soya beans give fat and oil.
Importance of Fat and Oil
It gives you energy even more than carbohydrates
It supplies essential fatty acids to the body.
It helps in the maintenance of body temperature
It provides the body with fat-soluble vitamins
MINERAL SALT
These are usually taken in very small quantity in the food we eat. The minerals include calcium, magnesium, potassium, Phosphorus, sulphur, chlorine, iron, Iodine, fluorine, manganese, copper, cobalt and sodium.
Importance of Mineral Salts
a. Regulate body metabolisms
b. Components of bones and teeth
c. Aids blood formation
d. Control chemical reactions in the body
e. Aids the formation of enzymes and pigment
VITAMINS
These are organic food substances needed by man and other animals in small quantity for normal
growth and development. Vitamins are grouped into:
1. Water-soluble vitamins include: vitamins B complex and vitamin C. Vitamin B complex include
vitamin, B2, B3 , B5, B6 and B12
2. Fat-soluble vitamins include vitamins A, D, E and K.
Importance of Vitamins
4. Support immune system
5. Enhances growth and development
6. It enhances vision.
WATER
This is of utmost importance to all organisms and it is made up of two elements, hydrogen and
oxygen.
IMPORTANCE OF WATER
a. Metabolic activities of the body of animals.
b. Digestion of food.
c. Maintenance of body temperature.
d. It is a medium of transportation for all nutrients.
e. It helps to maintain the osmotic balance in body tissues.
f. It helps in excretion of metabolic waste from the body e.g urine.
ROUGHAGES
These are indigestible fibrous materials got from vegetables, fruit, carbohydrates and proteins.
Importance of Roughages
3. It aids digestion
4. It helps to avoid constipation.
BALANCED DIET
Balanced diet is a diet containing a correct proportion of all the food substances. On a general note, a
balanced diet contains 15% protein, 15% fat and oil, 10% vitamin, minerals and water and 60%
carbohydrate. Once a food is taken at these proportions, there is a normal growth and development in
the body.
FUNCTIONS OF BALANCED DIET
1. It makes us healthy.
2. It gives ability to be resistant to diseases
3. It makes available energy needed to carry out all biological activities.
4. It prevents malnutrition and deficiency symptoms. For examples, a diet that lacks protein results into a nutritional disease called kwashiokor in children.
MAMMALIAN TEETH
TYPES OF TEETH
The teeth in mammals are of four major types:
1. Incisors: Flat, chisel-shaped with a sharp edge. They are used for biting food, cutting and holding
onto a prey to prevent its escape.
2. Canine: similar to the incisors. They are sharp and pointed at the tips. They are used for tearing
flesh and for catching a prey.
3. Premolars: They are large with rigid flat surfaces which are used for chewing food.
4. Molars: They are used for grinding and chewing food together with the premolar.
STRUCTURE OF A TOOTH
The mammal’s tooth is divided into three regions
The crown which projects above the gum
The root which is embedded in the jaw bones.
The neck which is the junction between the crown and the root
STRUCTURE OF THE TOOTH
The centre of the tooth consists of a pulp cavity which contains blood vessels and nerves. These are
extremely sensitive to heat and cold. A layer of dentine encloses the pulp. Dentine is a hard and
bone-like material which contains some living cytoplasm. The enamel is a white layer covering the
dentine and is the hardest material made by animals. Enamel protects the pulp and the dentine. A
layer of cement covers the dentine in the root region.
DENTITION
Dentition is the number, arrangement and conformation of teeth in an organism. The teeth are
arranged and fixed to the lower and upper jaw bone.
Types of Dentition
1. Homodont dentition: that is when organisms have the same type of teeth.. All the teeth are of the
same shape, size and function. This dentition is found in fishes, amphibians and reptiles.
2. Heterodont dentition: In this type, organisms have teeth of different shapes, sizes and functions. This observed in mammals.
The type of teeth possessed by an animal is closely related to the type of food it eats.
DENTAL FORMULA
A formula expressing the number and kinds of teeth possessed by a mammal. A dental formula is
usually written in the form of four ‘fractions’,
Man………….2[ I=2/2, C=1/1, P=2/2, M=3/3] = 32.
Dog …………… 2[ I=3/3, C=1/1, P=4/4, M=2/3] = 42.
Cow …………….2[ I=0/3, C=0/1, P=3/3, M=3/3] = 32.
Lion…………… 2[ I=3/3, C=1/1, P=3/2, M=1/1] = 30.
Rabbit …………… 2[I= 2/1, C= 0/0, P=3/2, M=3/3] =28.
Sheep …………….. 2[I=0/3, C=0/1, P= 3/3, M= 3/3] =32.
Rat …………….. 2[I=1/1, C= 0/0, P=0/0, M=3/3] = 16
DIGESTIVE ENZYMES
Enzymes are organic (protein) catalysts produced by living cells which help to speed up and slow
down the rate of chemical reactions. Digestive enzymes aid the breaking down of complex food
substances into simple, soluble and diffusible form.
Characteristics of Enzymes
a. Enzymes are soluble.
b. Enzymes are protein
c. They are specific in their actions
d. Enzymes are sensitive to temperature i. e. they work best between 35°C to 40°C
e. Enzymes are PH specific
f. Enzymes brings about reversible reactions
